PBMCs or Whole Blood? Strategic Applications in Phase I Studies
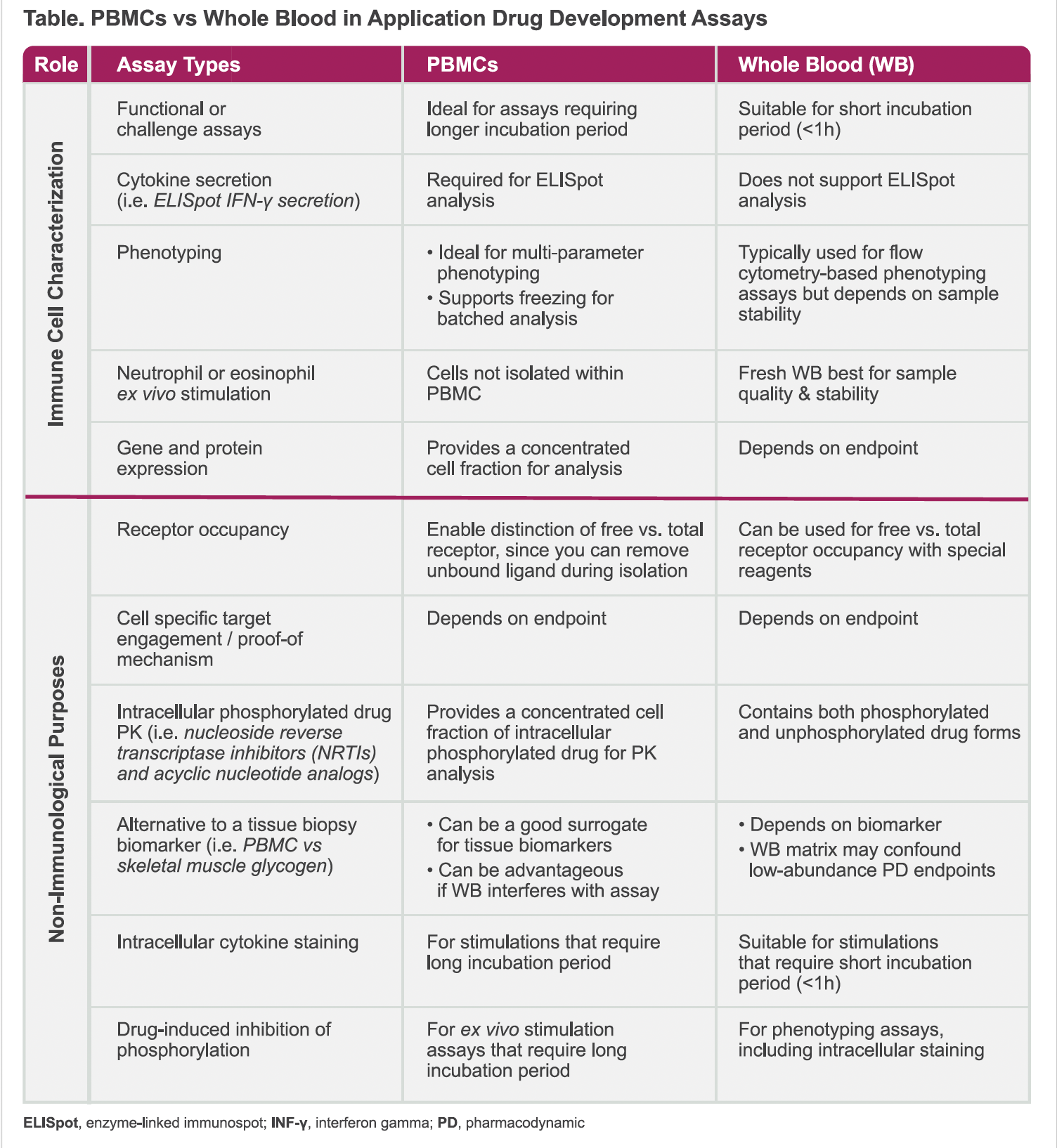
Studying peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) reveals cell-specific biomarkers—like target engagement and receptor occupancy—that improve decision-making in Phase I clinical trials. This makes these assays incredibly powerful tools in early-phase studies and has resulted in a growing trend of incorporating PBMC isolation and flow cytometry in Phase I clinical studies.
PBMCs are a group of white blood cells with a single nucleus, separated from whole blood through centrifugation. They include monocytes, lymphocytes, dendritic cells, T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
In this blog article, we’ll compare PBMCs and whole blood sample types and review their strategic applications in Phase I trials. We’ll also show how Celerion’s expertise in PBMC isolation and flow cytometry can accelerate your clinical program.
What Is Flow Cytometry?
Flow cytometry is a technique that measures cells in suspension. The cells are tagged with a fluorescent molecule that absorbs light at a specific wavelength and re-emits light at a longer wavelength. This can be leveraged to ‘gate’ or sort a specific cell population.
Why Choose PBMCs Over Whole Blood in Phase I Assays?
Whole blood contains red blood cells, PBMCs, platelets as well as hormones, lipids, proteins. While whole blood requires little initial sample handling compared to the PMBC isolation process. PBMC isolation can be advantageous, supporting several downstream analyses, such as ELISpot. In addition, the whole blood components may interfere with the assay and hinder stimulation or incubation of cells with targeted reagents, therefore PBMC isolation and appropriate cell culture environment are preferred.
Innovative Approaches to Clinical Pharmacology
Beyond immune characterization, PBMCs offer novel opportunities in clinical pharmacology. PBMC isolation and flow cytometry has traditionally been applied for immune cell characterization and biologics, however this procedure can also be leveraged for small molecules and for non-immunological purposes. In particular, PBMC isolation can support clinical pharmacology studies, for example:
- Deeper Insights: PBMCs can provide deeper insights into cell-specific target engagement and intracellular drug activity, enhancing the understanding of drug mechanisms and effects.
- Less Invasive Alternatives: PBMCs can potentially replace invasive procedures, such as skeletal muscle biopsies, by serving as surrogate biomarkers for tracking drug effects and activity.
- Versatility: PBMCs can be leveraged for small molecules and non-immunological purposes in addition to biologic drug development, expanding their applicability in various clinical pharmacology studies.
Our PBMCs Experts are Ready to Support your Next Study
These approaches and their strategic applications were discussed early this year with industry peers at the ASCPT 2025 conference in Washington, DC, highlighting the growing role of PBMC-based assays in accelerating early-phase drug development.
Celerion has experience with incorporating PBMCs into a variety of clinical pharmacology studies including SAD/MAD, bioavailability, food effect, drug-drug interaction (DDI) and renal/hepatic impairment, as well as bioanalytical support for late phase studies. At Celerion, our expert clinical pharmacology & bioanalytical team can help unlock your next study by gaining deeper insights with PBMC & flow cytometry technology.
